Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
- PRP is for those who have a healing mindset because it helps the body heal itself.
- It aids in healing wounds and alleviating pain through the injection of a patient’s own platelets, in high concentration, into an injured tendon, ligament, or muscle tear. The platelets contain growth factors that help stimulate natural healing.
PRP Research
- Platelets are blood cells that are instrumental in the healing process because they help one’s body stop bleeding. This involves the formation of blood clots, the release of growth factors, as well as the release of proteins. It also involves obtaining a patient’s own blood in a process known as “blood-spinning” to help with healing injuries.

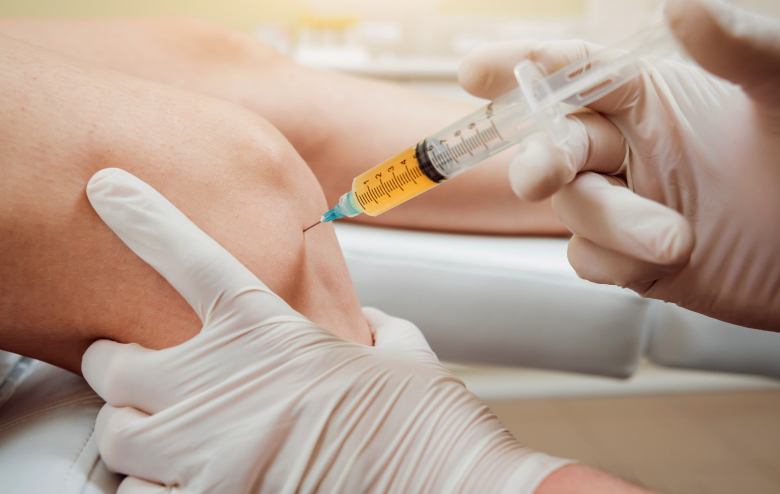
- PRP injections deliver biomolecules released by a concentrated pool of activated platelets to the site of injury. This effectively helps manage inflammation, angiogenesis, and the immune response. PRP at Allevio accelerates the healing process and repair time of injured tissues.
Different Types of PRP
- Two types of PRP options are available on-site. These include leukocyte-rich PRP and leukocyte-poor PRP.
- Leukocyte-rich PRP involves a higher count in white blood cells. It is used for muscle tears and tendinopathies. Leukocyte-poor PRP is specifically used for joints and spinal injections because they have a lower count in white blood cells.

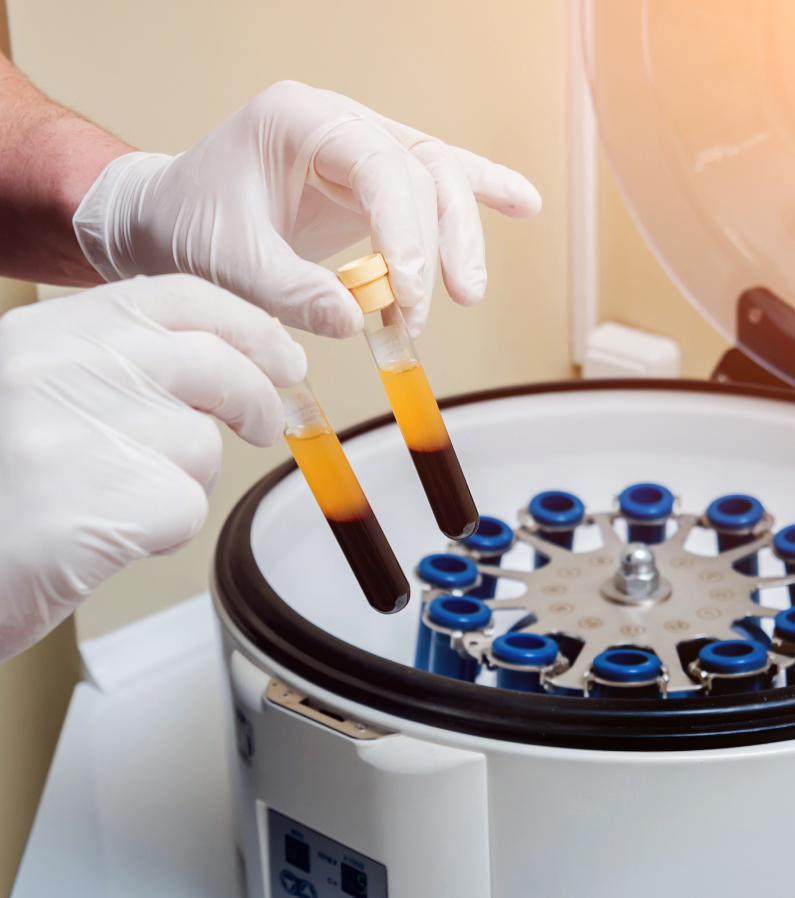
Side Effects of PRP Injections
- PRP treatments can provide advantages in clinical applications because they use the patient’s own blood. Advantages are also given through safety profiles, the ease at which the source can be obtained, and the minimally invasive application procedure itself.
- As injecting PRP involves using a person’s own platelets, they do not usually experience any adverse reactions.
