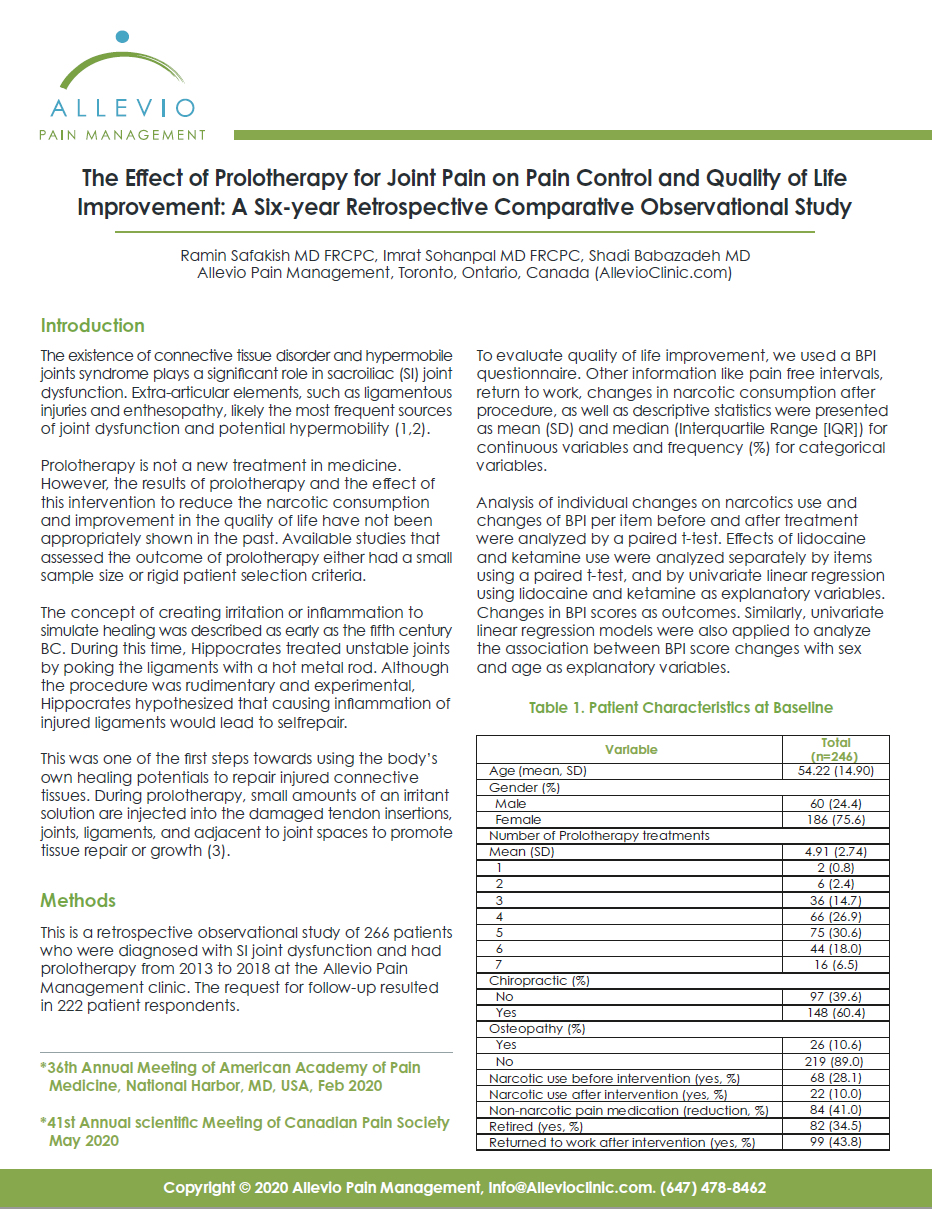
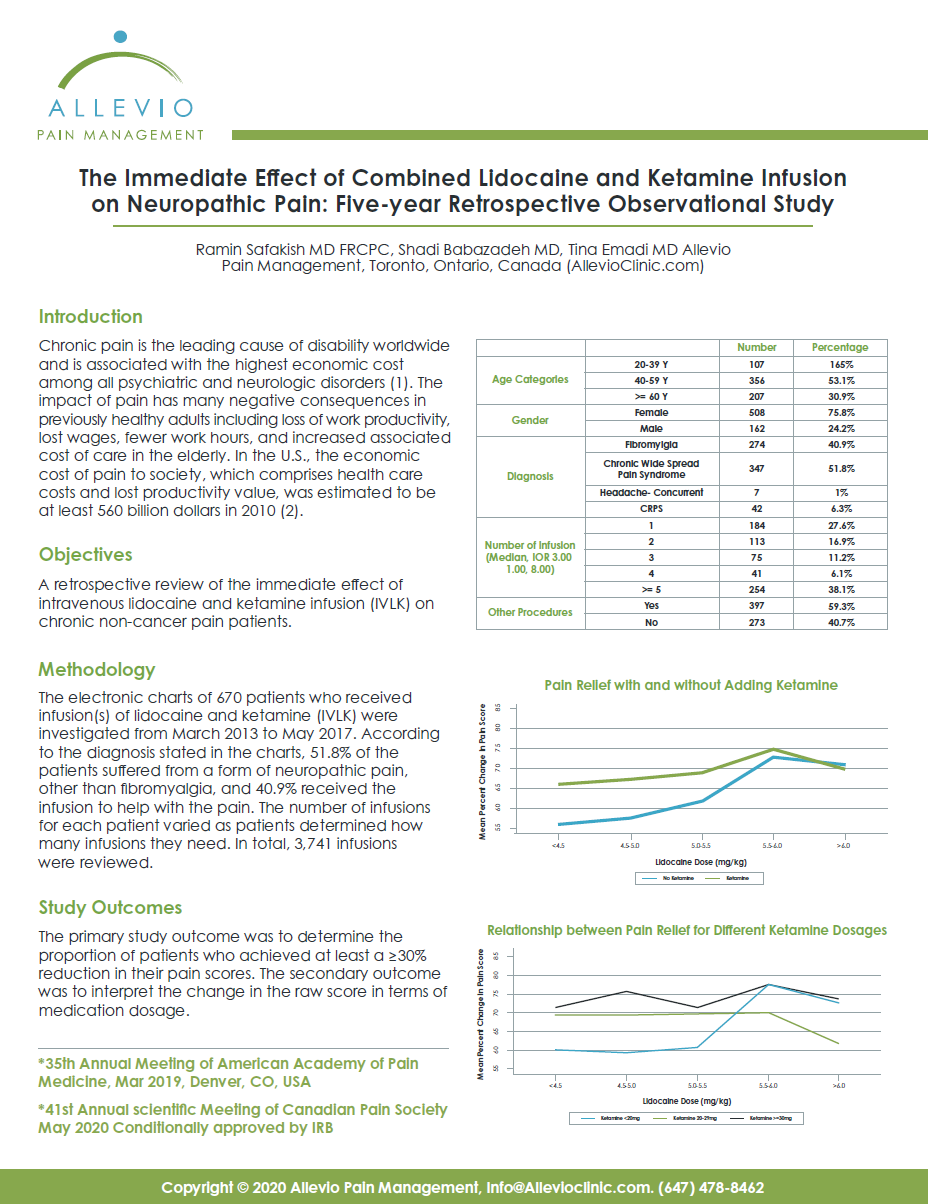
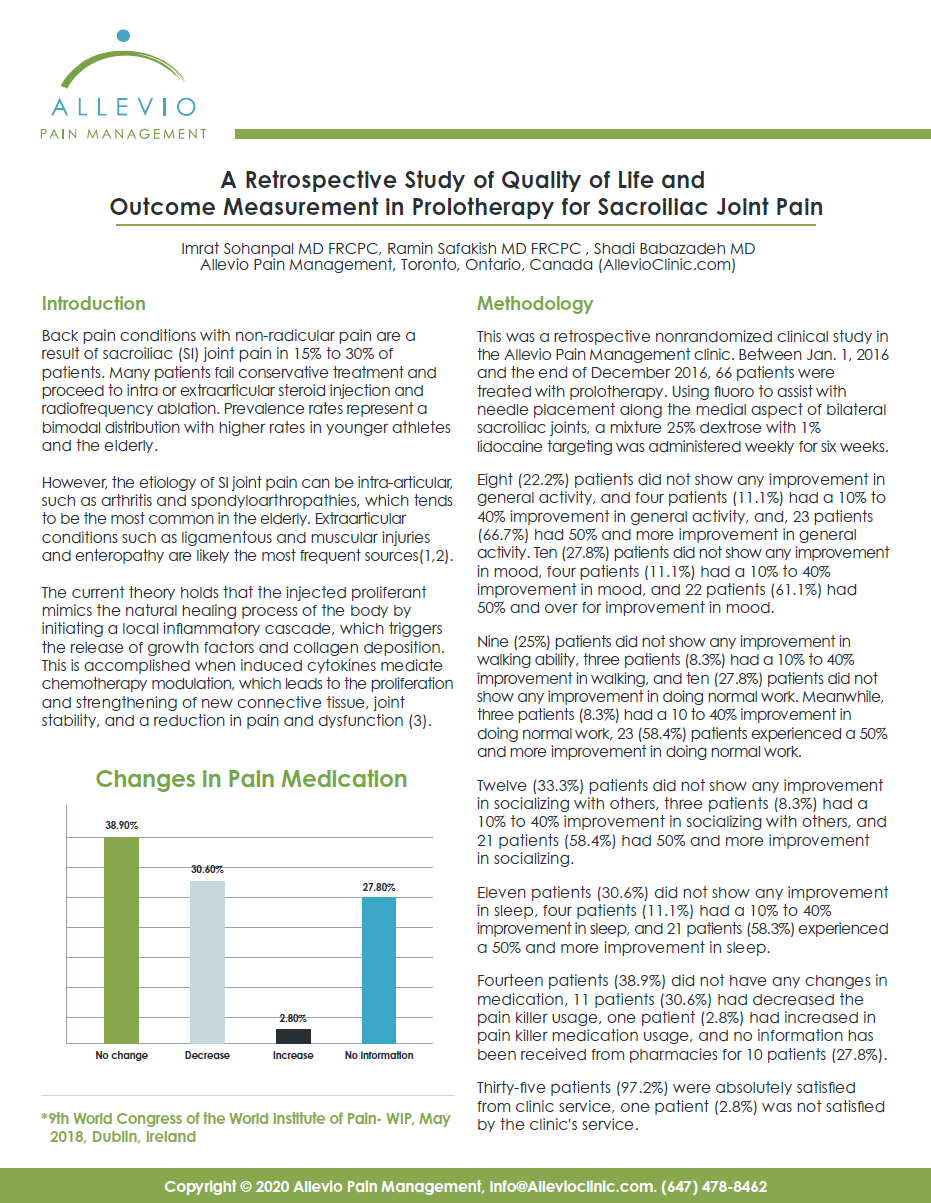
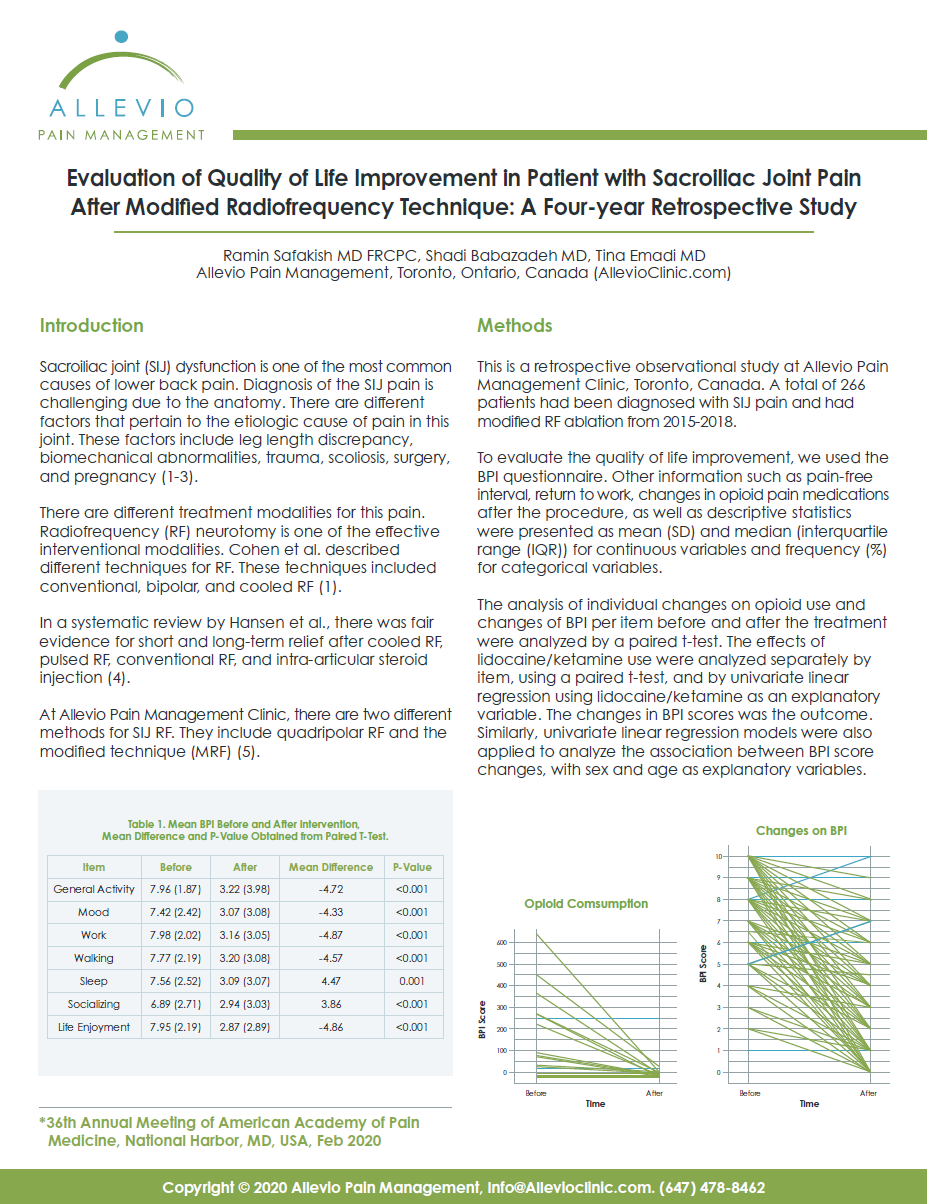
The Effect of Prolotherapy for Joint Pain on Pain Control and Quality of Life Improvement: A Six-year Retrospective Comparative Observational Study
The existence of connective tissue disorder and hypermobile joints syndrome plays a significant role in sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction. Extra-articular elements, such as ligamentous injuries and enthesopathy, likely the most frequent sources of joint dysfunction and potential hypermobility (1,2). Prolotherapy is not a new treatment in medicine. However, the results of prolotherapy and the e‑ect … Read more